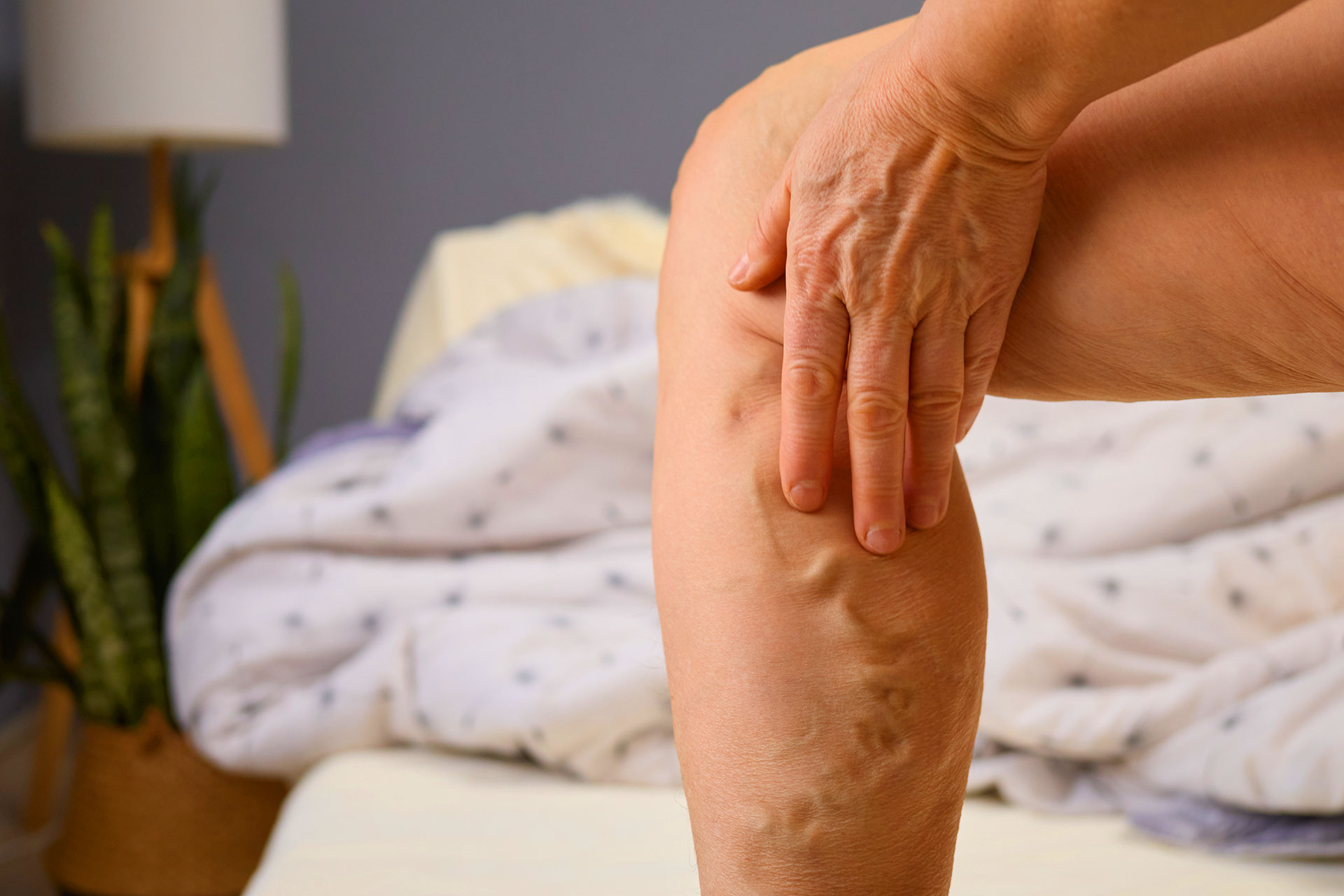
What Sets Varicose Veins Apart?
The distinct appearance, potential symptoms, complications, and diagnostic process set varicose veins apart from normal veins. Seeking medical advice for proper diagnosis and management is crucial for individuals with suspected varicose veins.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins exhibit various symptoms that are worth paying attention to. Symptoms include twisted veins, feeling heaviness in the legs, and pain. Diagnosis is based on a physical examination, including a family history of varicose veins and tests.
One of the main signs is swollen veins, which often appear as spider veins on the surface of the skin. Varicose veins occur when the valves in the veins weaken, allowing blood to pool. Varicose veins and enlarged veins can cause a feeling of heaviness, especially after standing or sitting
for long periods.
The appearance of venous ulcers and dark purple areas on the skin may also indicate varicose veins.
Female hormones, especially during pregnancy, can contribute to the development of varicose veins.
Bulging veins are a common characteristic of varicose veins.
If symptoms are detected, it is important to wear compression stockings, avoid sitting or standing for long periods, and seek prompt medical attention to determine the best treatment options and prevent complications.
Varicose Vein: Causes and Risk Factors
An essential step in the management of varicose veins is accurate diagnosis. A physical examination, including a review of family history, can help identify and understand a patient’s medical history and what to expect. The causes of varicose veins diagnosed:
- A blood clot in the veins can lead to complications like deep vein thrombosis.
- Over time, varicose veins develop due to weakened vein walls and faulty valves.
- Although rare, severe complications like pulmonary embolism can result from untreated
varicose veins. - Varicose veins can affect blood pressure in the affected areas.
- Leg veins, especially the larger ones, can be affected by varicose veins.
- Deep veins are also susceptible to varicose changes, leading to potential complications.
A damaged vein may lead to blood pooling and the formation of varicose veins, too.
Doppler ultrasound is commonly used to diagnose varicose veins and assess blood flow. Skin color, veins stretch and severity, the presence of ulcers, and symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency are evaluated by a physician.
How to Treat Varicose Veins
The treatment of varicose veins can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the symptoms experienced. Here are several common approaches to treat varicose veins:
- Engage in regular physical activity to improve blood flow and strengthen leg muscles.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the veins.
- Compression stockings can help improve blood flow and alleviate symptoms.
- Elevate your legs when resting to encourage blood flow back to the heart.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage pain associated with varicose veins.
- Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: These may be recommended to reduce inflammation
- Chemical Closure: A particular chemical is injected into the affected vein to close it off
- Healthy Habits: Adopt habits that promote good vascular health, such as avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing
Proper blood flow is essential to prevent varicose veins and maintain vascular health. If varicose veins affect the blood vessels, they will hinder the normal flow of blood.
Treatment for varicose veins can range from conservative methods, such as wearing compression stockings and lifestyle changes, to more intensive medical procedures.
Conclusion
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan for individual cases. Treatment choice depends on factors like the size and location of the veins, symptoms experienced, and overall health.